1. Minimum Spanning Tree
先来看看最小生成树的定义
Minimum Spanning Tree: Given a connected graph G = (V, E) with real-valued edge weights $c_e$, find a subset of edges T ⊆ E that connects all vertices and has minimum total weight.
用通俗的话来说就是给定一个连通图,找到一个边的子集,使得这个子集连接所有的顶点,并且具有最小的总权重。 注意:只有连通图才有生成树,而对于非连通图,只存在生成森林。

Cayley's Theorem:一个有 $n$ 个顶点的连通图有 $n^{n-2}$ 个生成树。
2. Greedy Algorithm of MST
解决 MST 问题有两种种常见的贪心算法,分别是 Kruskal 算法和 Prim 算法,这两种算法的定义如下:
Kruskal's algorithm: Sort edges by weight, and add them to T one at a time, from smallest to largest weight, unless doing so would create a cycle.
Prim's algorithm: Start with some root node s and greedily grow a tree T from s outward. At each step, add the cheapest edge e to T that has exactly one endpoint in T.
3 Cycles and Cuts
为了能够证明上面两种算法的正确性, 我们先来了解一下 环 和 割集 的概念。
Cycle :环是一个形成简单环的边的子集。

在上面这幅图中,边1-2,2-3,3-4,4-5,5-6,6-1组成了一个环。
Cut :一个割 $S$ 是图 $V$ 的一个子集。

Cutset :一个环 $S$ 对应的割集 $D$是仅有一个端点在 $S$ 中的边的集合。

从上述定义中,我们可以知道环和割集都是一个图中边的子集
我们先来看一下下面这些重要的定理
3.0 Cycle-Cut Intersection
A cycle and a cutset intersect in an even number of edges.
这条定理说的是,一个图中的环和割集会有偶数条相交的边。

我们能够通过下面这幅图来证明:
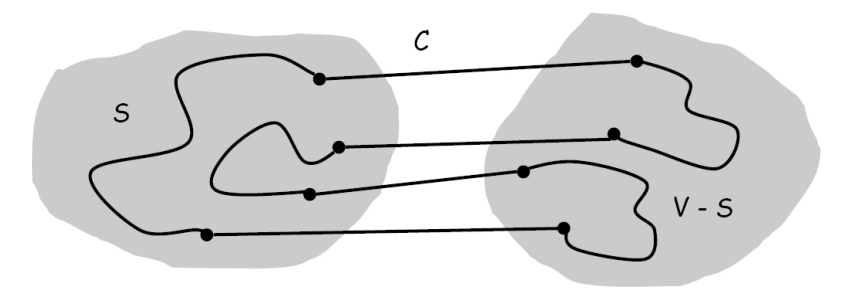
由于环 $C$ 中的点分布在集合 $S$ 和 $V-S$ 中,为了能够构成一个环,从 $S$ 到 $V-S$ 的边的数量必须等于从 $V-S$ 到 $S$ 的边的数量,因此环 $C$ 和割集 $D$ 相交的边的数量必须是偶数。
3.1 Cut property & Cycle property

Cut property:令 $S$ 为任意节点的子集,令 $e$ 为 $S$ 对应的 Cutset $D$ 中的最小成本边。那么 MST 包含 $e$。
证明:反证法,假设 $e$ 不在 MST 中。我们将 $e$ 加入到 MST 中,这样就会形成一个环,此时,$e$ 这条边在环 $C$ 和割集 $D$ 中,由于 $C$ 和 $D$ 的交集是偶数条边,因此一定存在一条边 $f$,使得 $f$ 在环 $C$ 中也在割集 $D$ 中。此时,我们将 $f$ 从 MST 中删除,这样就会得到一个更小的生成树,这与 MST 的定义相矛盾,因此假设不成立,$e$ 必然在 MST 中。 sdf
Cycle property: 令 $C$ 为任意环,令 $f$ 为 $C$ 中的最大成本边。那么 MST 不包含 $f$。
Cycle property 的证明方法其实和 Cut property 的证明思想是一样的,都可以使用反证法,这里就略过了。
4. Prim’s Algorithm
Prim’s Algorithm 算法是 Prim 在 1957 年提出的,这个算法的思想是从一个点开始,每次选择一个与当前生成树距离最近的点加入到生成树中,直到所有的点都加入到生成树中。我们可以根据Cut property来证明该算法的正确性。
- Initialize S = any node.
- Apply cut property to S.
- Add min cost edge in cutset corresponding to S to tree T, and add one new explored node u to S.
5. Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal’s Algorithm 算法是 Kruskal 在 1956 年提出的,这个算法的思想是从一个点开始,每次选择一个与当前生成树距离最近的点加入到生成树中,直到所有的点都加入到生成树中。我们可以根据Cycle property来证明该算法的正确性。
- Consider edges in ascending order of weight.
- Case 1: If adding e to T creates a cycle, discard e according to cycle property.
- Case 2: Otherwise, insert e = (u, v) into T according to cut property where S = set of nodes in u’s connected component.